Understanding Radon Gas: What Is It and How It Affects Life and How to Prevent Hazards from Radon?
When it comes to invisible threats lurking in our homes, radon gas stands out as one of the most prevalent. This naturally occurring radioactive gas can have significant health implications if not properly managed. In this article, we will explore what radon gas is, how it impacts health, and crucially, the steps you can take to prevent its hazards.
Understanding Radon Gas
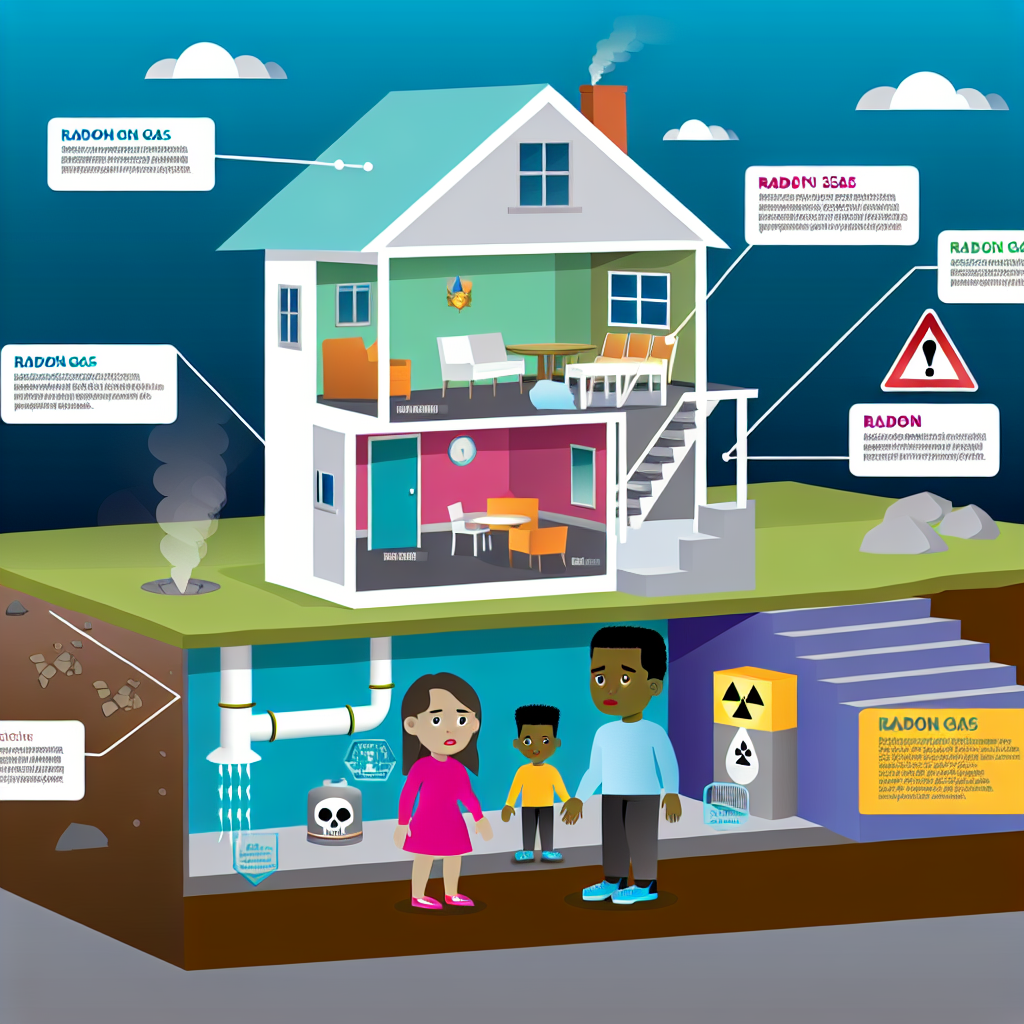
Radon gas is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless radioactive gas that emerges from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock, and water. It infiltrates homes through cracks and openings in the foundation, accumulating over time if ventilation is insufficient.
Where Does Radon Come From?
- Soil and Rock: The main source is the uranium decay chain present in many soils and rocks worldwide.
- Groundwater: Radon can dissolve into water and release into the air during everyday activities such as showering.
- Building Materials: Some materials, like granite, can release radon, although it is typically less significant.
Radon levels can be higher in certain geographic locations, especially in areas with abundant granite or shale subsoil, leading to regional variability in exposure risks.
How Radon Affects Life
The health effects of radon exposure are disconcerting and medically significant, primarily because of its carcinogenic potential.
Health Risks Associated with Radon
- Lung Cancer: Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. It is responsible for approximately 21,000 deaths per year in the United States alone.
- Increased Risk for Smokers: Smokers exposed to elevated radon levels face even greater risks of developing lung cancer.
- Other Potential Risks: Although less conclusive, studies are ongoing to determine radon’s connection to other respiratory conditions and cancers.
Continuous exposure over time increases the likelihood of adverse health effects, highlighting the need for awareness and action.
Preventing Radon Hazards
Testing for Radon in Your Home
Understanding your home’s radon levels is the first step in mitigation:
- Short-Term Testing: Affordable and easily accessible, short-term radon test kits available at hardware stores can provide a snapshot of your radon levels.
- Long-Term Testing: For a more accurate annual average, long-term test kits placed for 90 days or longer are recommended.
- Professional Testing: Engaging certified radon professionals to conduct a detailed assessment can ensure precise results.
Radon Mitigation Strategies
If testing reveals high radon levels, several mitigation strategies can reduce the risk:
- Sub-Slab Depressurization: This is the most effective method for reducing radon levels, which involves a system that vents radon from beneath the home to the outside.
- Improving Ventilation: Enhancing natural air circulation within the home helps dilute radon concentrations.
- Seal Openings: Sealing cracks and openings in floors and walls can help reduce radon entry.
- Positive Pressure Ventilation: Special systems can be installed to slightly pressurize the building, preventing radon entry.
Regular Monitoring
Once mitigation measures are in place, regular monitoring is essential to ensure their continued effectiveness. It’s advisable to test your home every two years, or more often if you have made significant changes to your home or its ventilation system.
Conclusion
Radon gas may be invisible, but its impact on health is undeniable. Understanding its origins, health implications, and mitigation strategies is crucial in safeguarding your family’s health. By conducting regular testing and implementing effective mitigation solutions, you can effectively reduce radon exposure in your home, ensuring a healthier indoor environment. Stay informed, stay safe, and breathe easier knowing you’re taking active steps against this silent threat.
